Gum surgery, often referred to as gingival surgery within the dental and oral surgery field, is a procedure intended to treat gum disease and improve the physical appearance of a patient’s smile. It could be considered an elective surgery when it is performed for cosmetic reasons, or it can be considered medically necessary in the event that the patient is suffering from severe gum disease and has lost or nearly lost functionality of his or her teeth and gums.
Types of Gum Surgery
There are numerous varieties of gum surgery commonly performed by experienced oral maxillofacial surgeons, but most types fall into one of four general categories.
- Pocket reduction surgery involves the folding back of the gums and the removal of any bacteria that has accumulated beneath them; once bacteria has been removed, an oral surgeon will then re-secure the gum tissue to the patient’s teeth to prevent bacteria regrowth.
- Gum regeneration procedures are similar to pocket reduction surgery, but also involve the insertion of bone grafts, tissue-stimulating proteins, or membranes intended to encourage gum tissue regeneration.
- Soft tissue grafts may be required when a patient’s gum loss is severe. This procedure involves the removal of tissue from other places in the patient’s mouth and its attachment to areas where gum tissue has significantly receded.
- Crown lengthening, on the other hand, requires oral surgeons to remove excess gum tissue from the mouth, making teeth appear longer; this surgery is more frequently used for cosmetic purposes than the medical treatment of gum disease.
Recent innovations within the field of oral surgery have led to the use of laser therapy in treating gum disease as well. Laser surgery falls somewhere between root scaling and planing and the traditional surgeries listed above in terms of invasiveness. During a laser procedure, an oral surgeon will use a specialized periodontal laser to access and easily remove any inflamed gum tissue present around the root of the tooth, then perform root scaling using traditional instruments to remove any existing plaque and tarter calculus, and then smooth out any rough spots that could encourage bacterial growth. The main benefit of laser gum surgery is less downtime.
Reasons for Having Gingival Surgery
As noted above, the majority of gum surgeries are performed to address severe forms of gingivitis; however, it may also be required after a failed root canal to seal the root against further bacterial damage and to prevent the spread of infection. Those suffering from excessive gum sensitivity or inflammation, gum recession unrelated to periodontal disease, excessive bleeding, or halitosis, may also benefit from this surgery. Patients may also elect to have cosmetic surgery performed on their gums in order to improve the appearance of the gum lines by removing extra or asymmetrical tissue.
Benefits of Gum Surgery
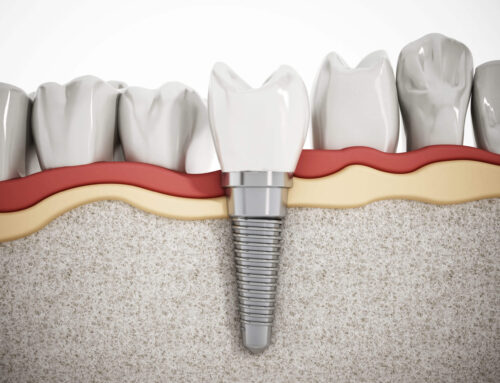
The primary benefits of gum surgery are, of course, improved oral health through the elimination of bacterial colonies, and also improved appearance. Patients who are undergoing gum surgery to address severe forms of gingival disease will also find it helps them maintain their overall health by reducing their risk of heart disease, stroke, and a wide variety of other conditions. It may also eliminate bad breath, and assist with the preservation of the patient’s teeth and jawbone. Moreover, if teeth have been lost due to gum disease, the beauty of working with the highly-trained dental practitioners of OMSH, is that they can professionally install dental implants after gingival surgery to replace missing teeth and restore your natural smile.
Your Gums in Professional Care
If you’re interested in learning more about dental implant options and the various restorative surgeries offered by OMSH in Houston, connect with us at tel:832-509-4505. Schedule your consultation and speak with one of our dedicated oral maxillofacial surgeons to discuss your options.